
- #Intel rapid storage technology rst update install
- #Intel rapid storage technology rst update windows
Next, you will need to display the list of volumes, make sure the volume that contains Windows is correctly assigned the letter C: (if it’s not, you will need to change this), make this volume active, and then run the boot repair command. The first step is to run the disk partition tool to see and understand the disk layout. This will launch the Windows command prompt, where you can run commands to diagnose and repair problems, including boot-related issues. Under Choose an option, select Troubleshoot. On the screen that gives you the result of the Automatic Repair, click on Advanced Options. Windows will attempt to restart and automatically diagnose and repair the boot-related problems, but it will most likely not be able to complete the task itself, and you will need to manually launch the command prompt from the recovery screen, and fix the issue. You will most likely see a blue screen with a Stop code: INACCESSIBLE BOOT DEVICE. In this case, you will need to recover your Windows. For instance, this could happen if you made the BIOS change without making the registry changes in Windows.
#Intel rapid storage technology rst update install
It should read: Standard SATA AHCI Controller.Īfter making the necessary changes to allow Ubuntu to install side by side with Windows, you may encounter a situation where Windows no longer boots. Windows should load normally, and you can check the controller mode in the Device Manager. The exact terminology and steps required to access and manage controller type in BIOS often depend on the specific implementation by the platform vendor.Įxit BIOS, and let the system boot.

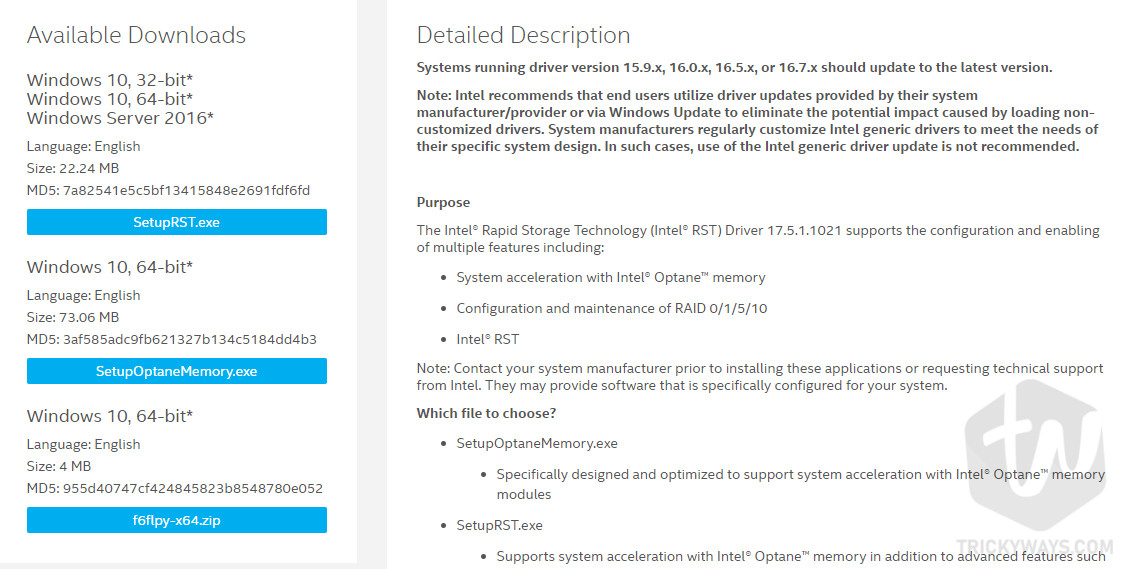
In the BIOS menu, change the hard disk controller type to AHCI. Normally, BIOS is accessed by hitting the F2 or Del key during the early boot sequence. Once this step is complete, reboot Windows and start your computer’s BIOS. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\storahci\ Repeat this set of changes for the following path in the Registry Editor: Next, double-click on the iaStorV entry in the left column to expand it, select the StartOverride entry, and then in the right column, change the value of the key 0 to 0. Here, in the right column, double-click on the Start key, and change its value to 0. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\iaStorV\ This can be done using the Registry Editor. If the controller mode is set to anything other than “Standard SATA AHCI Controller”, then you will need to make a change that allows Windows to boot safely in AHCI mode. You can do this through the Device Manager. Verify which controller mode is in use in Windows. Even simply copying the important files to an external drive can minimize the risk of data loss. You need to make sure your personal data is safe. Possible installation scenariosīroadly, there are two main configurations you may encounter when you try to install Ubuntu on a computer that supports and uses RST:īack your data up - any hard drive structure or configuration change, or installation of new operating systems on a hard drive that already contains data can potentially lead to a data loss. If you disable RST in the BIOS or change the RST configuration, Windows may become unbootable, as it may no longer be able to find and use the hard disks. For instance, Dell computers may have different settings from Lenovo or HP computers.įurthermore, you may already have Windows installed on the computer that uses RST. The exact terminology and steps required to access and manage RST in BIOS often depend on the specific implementation by the platform vendor. If the Ubuntu installer cannot detect the hard disks you need, then before you can install Ubuntu, you will need to turn RST in the computer’s BIOS. If you intend to install Ubuntu on a computer that supports RST functionality, you may need to make operational adjustments to your setup before you can proceed.īy default, the Ubuntu installer can detect certain RAID configurations, but it may not necessarily be able to access and use the hard disks grouped in them. RAID offers multiple configurations - levels - which focus on performance and redundancy.Ī complete user guide is available through the official Intel documentation. In some usage scenarios, RAID offers various advantages over the use of several disks independently. This functionality is known as the Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID). On platforms that have RST support built and enabled in the computer’s BIOS, it allows users to group and manage multiple hard disks as single volumes. Intel Rapid Storage Technology (RST) is a solution built into a range of Intel chipsets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
